The surface characteristic values used by AERSURFACE are based on the land use classification by season. In the AERSURFACE User’s Guide, five seasons are used as defined below:
Seasonal Categories
| Category | Description |
| 1 | Midsummer with lush vegetation |
| 2 | Autumn with unharvested cropland |
| 3 | Late autumn after frost and harvest or winter with no snow |
| 4 | Winter with continuous snow on ground |
| 5 | Transitional spring with partial green coverage or short annuals |
When using AERSURFACE, the user can assign each calendar month to a season or else a default assignment is made. The default is the alignment of calendar months to calendar seasons.
Having lived most of my life in Texas, I know that seasons, particularly summers in Texas, are not evenly distributed throughout the year. Though the seasons are defined, the user’s guide offers no procedure in making the assignment of months to seasons.
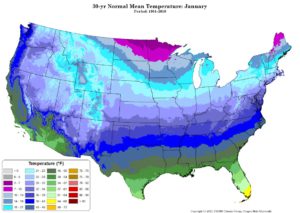
In keeping with the desire to obtain realistic and reproducible surface characteristic values for AERMET, we at NaviKnow are making a proposal for making the assignment of months to seasons using monthly mean temperature (1981-2010) at a location as follows:
- Winter – < 32˚ F
- Late Autumn – >32˚ and < 50˚
- Spring – > 50˚ and < 70˚
- Summer – > 70˚
- Autumn – < 50˚
The rationale is, if the monthly mean temperature is below freezing, odds are there is snow on the ground and the snow persists. If the temperature is above freezing but not that warm, then vegetation would be dormant and not growing. Once it get warmer, then new vegetation would grow. When the temperatures get even warmer, then we are into summer.
A reputable source of mean temperature data for the USA is http://www.prism.oregonstate.edu/normals/.
If you have any comments or suggestion on this proposed procedure to assign calendar months to seasons, please drop us a line at [email protected]. We want your feedback so we can create better products for you to do your job.
